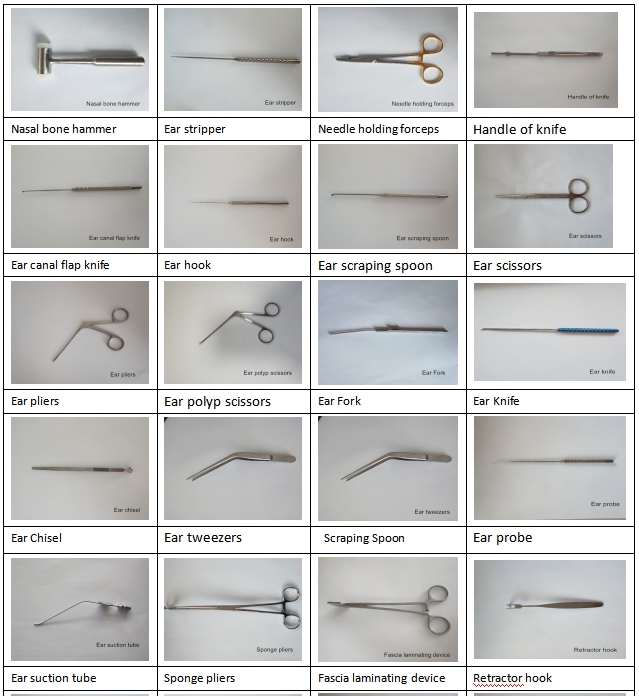
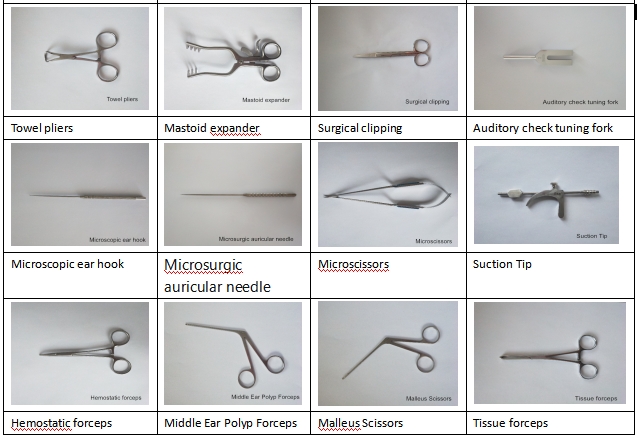
Ear hook is a multi-purpose hook tool, which pays attention to precision and durability. It is used in otological surgery, and strict sterilization is required
![]()
Ear hook is a multi-purpose hook tool, which pays attention to precision and durability. It is used in otological surgery, and strict sterilization is required.

Material and design features
Material: mainly using medical stainless steel or titanium alloy, both corrosion resistance and mechanical strength, part of the blade using carbon steel to enhance sharpness
Structure: Most of the instruments are designed to be detachable, which is easy to clean and sterilize. Precision instruments, such as ear endoscopes, should be protected from collision and moisture
Use and maintenance points
Sterilization requirements: Ear instruments should be sterilized by high temperature and pressure steam (132-134℃, 0.21-0.22MPa, 30 minutes) or low temperature plasma (50 minutes), and precision parts (such as endoscopes) should avoid chemical immersion
Aseptic operation: strictly distinguish between sterile and sterile areas, suction tubes and other instruments that contact with body fluids should be washed in real time to prevent blockage
Force control: to avoid excessive force leading to deformation of the instrument (such as ear bone chisel) or damage to the ear canal mucosa; The microscopic instruments should be handled gently to prevent collision
Cleaning and drying: immediately after the operation, wash the blood with running water, the lumen instruments (such as suction tube) should be cleaned thoroughly with a soft brush, and the motor parts of the ear drill should not be washed by high-pressure water gun. All instruments must be thoroughly dried to prevent corrosion
Lubrication and rust prevention: the joint area is coated with medical lubricating oil (such as mastoid chipper), and the titanium alloy instrument can be regularly maintained with paraffin oil
![]()
The material selection of ear surgical instruments emphasizes corrosion resistance and biocompatibility, and the structural design emphasizes delicacy and ergonomics. Aseptic operation standards should be strictly followed in use, and cleaning, drying and lubrication should be paid attention to during maintenance. The clinical scenarios cover tympanic membrane repair, mastoid surgery and foreign body treatment, etc., and the suitable scheme should be selected according to the characteristics of the instrument. Regular maintenance and professional training are the keys to prolong the life of instruments and ensure the safety of surgery
Myringoplasty :The tympanic membrane was incised with a tympanic knife (straight knife or scimitar knife), the lesions were trimmed with a micro-ear scissors, and the repair materials were clamped with a geniclike tweezer
Mastoid chipping:The mastoid chisel was used to remove the diseased bone, the mastoid rongeur was used to trim the edge, and the suction tube was used to remove the crushed bone and secretion
External Otitis Canal Plasty:The tumor was removed with an ear ring cutter, the adhesion tissue was separated with a dissector, and the surgical field was observed in real time with an ear endoscope.
Chronic otitis media:The pus was drained with an ear suction tube, the granulation tissue was harvested with a micro ear clamp, and the bleeding spot was coagulated with a laser system
Foreign body extraction from the ear:Knee-shaped forceps are used to remove foreign bodies (such as cerumen, insects) stuck in the ear canal, and an elbow suction tube is used to assist in cleaning.

Contact: Ms.Ye
Phone: 18030057721
E-mail: info@xmekoda.com
Whatsapp:008618030057721
Add: Torch High-tech Zone(Tongxiang) Industrial Base,Xiamen,China